Our Other Warehousing Services
Typcial Conventional Types Of Storage Systems
Standard Shelving
Wire shelving offers a flexible open construction and versatility that has the benefit of not collecting dust or block sprinkler systems. It’s attractive for use in many applications where more industrial-style shelves might be out of place. Numerically calibrated grooved posts, tapered plastic split sleeves and shelf collars adjust on 25mm centres for easy configuration.
Metal Clip standard shelving has solid metal shelves, in open or closed frame types. Metal shelving is the most easily accessorised shelving. It’s able to accept bins, modular drawers, various dividers, doors, and other modifications. It is a flexible system accommodating 6, 7 or 8 shelves, but more can be added or removed, depending on the stored product size and other requirements. LPC use a model to identify the slot sizes required by different SKUs and their order profiles and we would then specify the most suitable type based on the product’s physical needs and fire requirements etc.
Standard Adjustable Pallet Racking (APR)
Easily installed, cost effective and versatile, adjustable pallet racking (APR) in a wide aisle format of circa 3m is probably the most widely used of pallet storage systems allowing direct access to each pallet stored to beam heights of circa 12m.
With adjustable beams, racking can be re-configured to accommodate changes in the type of goods stored with access by virtually all types of fork truck, dependent on aisle width and height, making specialised handling equipment, unnecessary unless beam heights, for example, of 12m or greater are required.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | Required | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | |||||
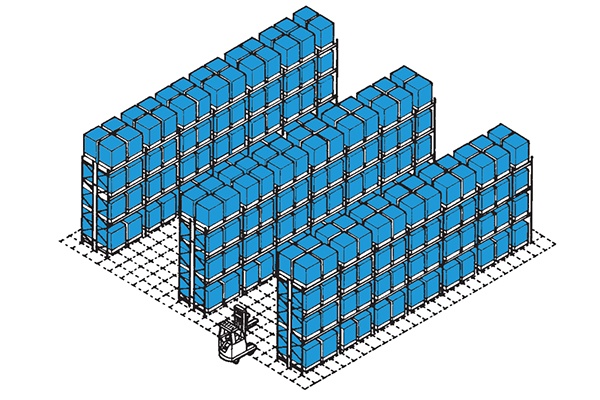
Double Deep Racking
Double deep pallet racking is the storage of pallets two deep with pallets accessed from the same side from the same aisle. Rate of access is restricted to all pallet positions and should be compensated with an efficient warehouse management system but the number of access aisles is reduced providing more storage space. This is a simple variance of standard wide aisle adjustable pallet racking which we would consider especially when re-engineering existing warehouses for greater capacity and or where product profiles allow its use without compromising efficiency too greatly. It is also certainly considered for automated systems when high bay cranes are used where there is, and would be, for the planning horizon, spare capacity for the crane use as storage capacity is considerably improved over single deep racking.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | Required | ||||
| Ease of relocation | |||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | |||||
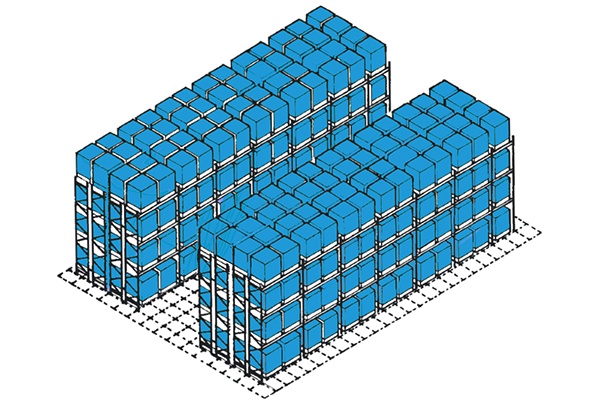
Narrow Aisle – Man Down
Very narrow aisle racking provides the most space-efficient pallet storage systems for direct access to individual pallets, with working aisles reduced to the absolute minimum to save floor space and pallets stored generally to heights of 14metres.
They can be operated with man down stacker trucks as shown below or with man up trucks. Both types are typically fixed path or directed movement trucks and are guided either by guide rails or with a wire guidance system – this allows for fast in aisle movement and much reduced risk of damage to racking.
Man down trucks only handle pallets and picking from pedestrian trucks in aisles needs strict control and is constrained by the reduced aisle width and something we would not normally recommend.
The trucks are also constrained in general to only handle pallets within these aisles as they are more expensive and only efficient when operating as designed. Pallets are ferried to them via Pick and Drop stations (P&Ds) by less expensive PPTs, Counterbalance trucks or Reach trucks dependent on requirement. These systems we have employed where automation is not wanted but easy access to all pallets is required for a bulk pallet store.
Free movement trucks such as the Bendi or Flexi can work in these aisles but are constrained by the weights they can lift to the upper levels. One advantage of these truck types is that they can also act as counterbalance trucks albeit with tall masts.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | Dedicated Trucks | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | |||||
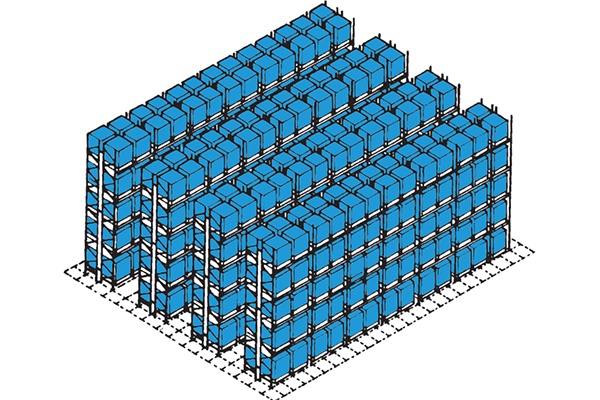
Narrow Aisle – Man Up
Very narrow aisle racking can be operated with man up (Combi) stacker / pick trucks as shown opposite or with man down truck as previously shown, both types are typically fixed path or directed movement trucks and are guided either by guide rails or with a wire guidance system – this allows for fast in aisle movement and much reduced risk of damage to racking.
Man up trucks can handle pallets and picking negating the need for either separate specific man up pick trucks or pedestrian trucks which need strict control and are constrained by the reduced aisle width. The trucks are also constrained in general to only handle pallets within these aisles as are more expensive and only efficient when operating as designed. Pallets are ferried to them via Pick and Drop stations (P&Ds) by less expensive PPTs, Counterbalance trucks or Reach trucks dependent on requirement.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | Dedicated Trucks | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | |||||

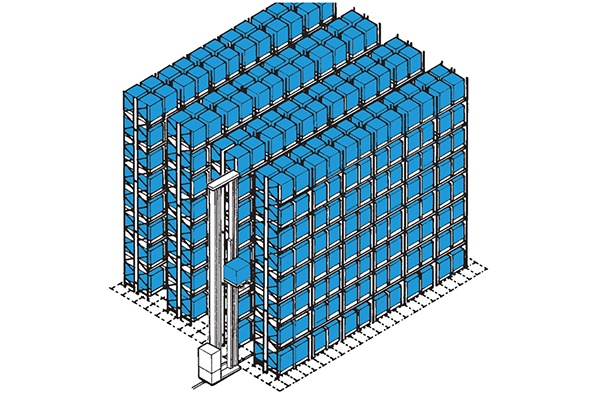
Very Narrow Aisle High Bay – Crane Served
Very narrow aisle and crane-served high bay racking provides the most space-efficient pallet storage systems, with working aisles reduced to the absolute minimum to save floor space and pallets stored generally to heights of up to 30+ metres.
As part of an integrated warehouse operation, these racking systems are served by order picking stacker cranes – typically fixed path – providing fast throughput and high accuracy in storage and retrieval.
A variant on APR racking allows pallet to be stored two deep but still accessible from the same side.
By reducing the number of access aisles and using the space saved to accommodate additional racking, double deep provides a highly space-efficient storage system.
Although the speed of access to all of the pallet positions is restricted, with an efficient stock management system (WMS) this can be compensated to take advantage of the benefits of more storage space.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads* | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | Required | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | Very Difficult | ||||
* Unless using double deep racking
Drive In Racking
Using minimal space for access aisles and lanes providing a high density and very space efficient bulk storage system.
With the first pallet into a lane being the last out (FILO), stock selectivity is heavily restricted, but when loads are despatched in batches, this is not a difficulty. However utilisation in a working lane is restricted.
Pallets are stored on beams in the depth of the racking and trucks drive in to deposit or retrieve loads.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | None Required | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | |||||
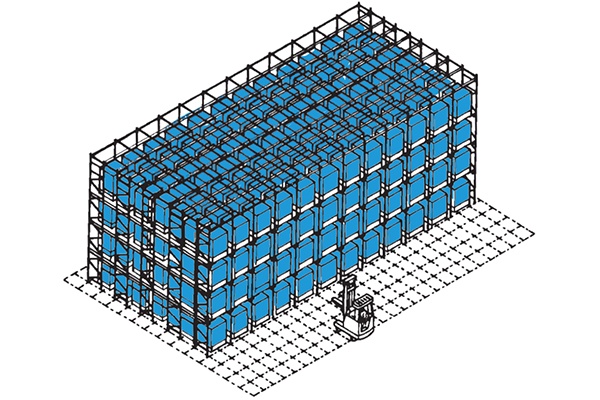
Push Back Pallet Racking
Dynamic push back pallet racking is amongst the most space and time-efficient pallet storage systems available. Typically used for bulk storage and in marshalling areas on a first in – last out basis with each stock keeping unit ideally having a dedicated lane.
Pallets can be stored two to six pallets deep, although three and four deep are more common, and are loaded in sequence onto wheeled carriers of differing heights or widths and are pushed back along inclined steel guide channels to utilise the full depth of the push back racking system. When a load is retrieved the remaining pallets roll forward into position at the picking face.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | None Required | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
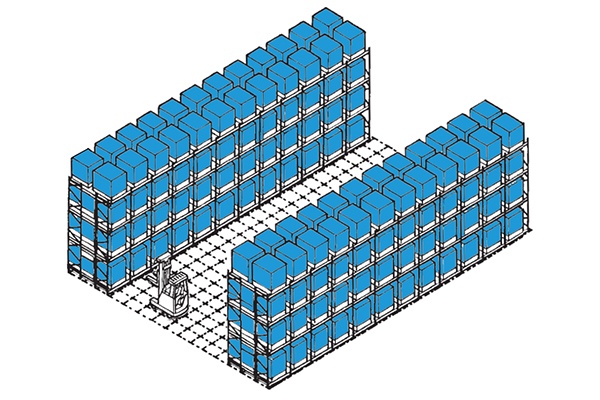
Mobile Racking
Easily configured for space saving mobile storage, maximum amount of space can be utilised for storage.
The racking is mounted on mobile chassis which move along guide tracks set into the floor, the floor space for only one ‘moving’ operating aisle is required to access all pallet location a defined number of rack rows which is a factor of the number of accessions required.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | None required | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | |||||
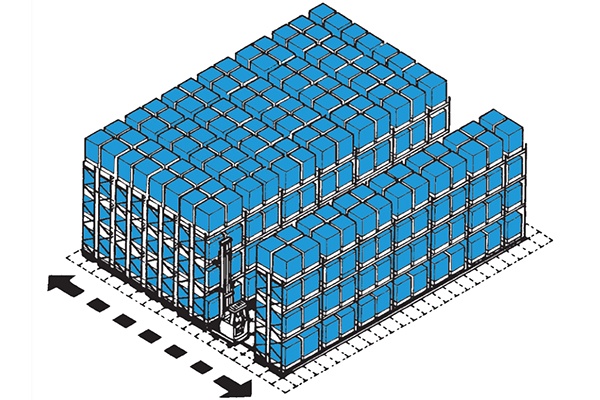
Pallet Live Racking
Pallet live racking provides high density storage whereby pallets are inserted into dedicated lanes on inclined gravity rollers. The front pallet provided the picking face and when picked the pallet behind rolls forward to replenish the pick face. Replenishment stock is loaded from the opposite aisle.
Pallet movement is managed by brakes and controllers that are fitted in the roller tracks. Providing a high level of storage density the stock is managed on a first in first out basis providing automatic stock rotation. Perhaps more useful for larger numbers of pallets per SKU and fewer SKUs. Also we have utilised pallet live racking to increase marshalling capacity (or reduce footprint)
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of storage area | |||||
| Utilisation of cubic storage space | |||||
| Access to individual pallet loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock rotation | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | Not Required | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | Not required | ||||
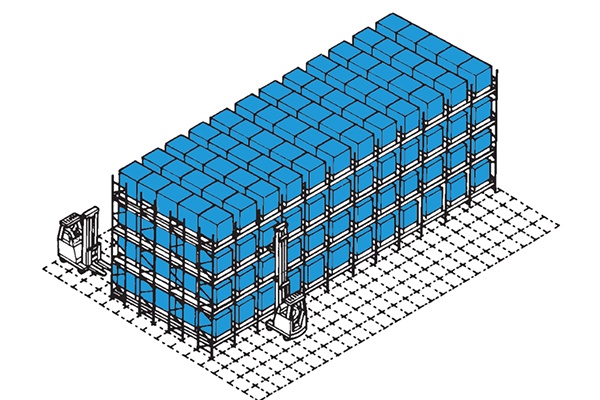
Carton Live Racking
Like pallet live storage, carton live racking is designed on inclined roller tracks on pre-determined storage levels whereby goods are stored in dedicated lanes and roll under gravity. The system is used for stock keeping units that are required to be picked by hand.
Carton (can also be tote) live racking is also known as flow racking and offers reduced picking times and errors as product is presented precisely at the picking face. The system works on ‘first in – first out’ principles and is efficient in space usage and fast moving product lines.
We employ this system when we need fast picking often for faster moving products as a dense pick face is provided with greater depth of stock behind every location than would be provided than by say a shelving pick face. There is also the added advantage that replenishment can occur simultaneously with picking without conflicting either operation.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of storage cube | |||||
| Access to individual carton loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock control | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | None Required | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | |||||
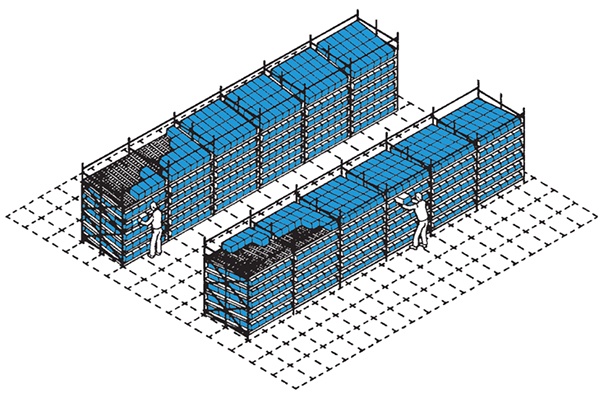
Shuttle Racking
Also termed as moles, pallet runers etc. this is similar to drive-in racking, the shuttle system allows for more pallets to be stored in a given area when compared to conventional static racking and gives much higher utilisation and operational efficiency than drive in.
Accessibility is increased as all levels of racking can be accessed at any time. The loading of the pallet in each tunnel can be done with a conventional Reach Trucks, counterbalance or with Narrow Aisle Trucks and highbay cranes or other automated variants.
The pallets are moved inside the “tubes” (tunnels) by a shuttle operated by remote control and equipped with photocells that position the shuttle under the pallet in the tunnel.
We have utilised this style of storage when re-engineering existing warehouses to increase pallet capacity and is especially efficient when implementing into a building grid designed for other types of storage systems. As the storage is level (not sloped as in Pallet Live) lanes can be used from both ends (potentally spreading work in different aisles) and as FIFO for whole lane lengths or FILO for less than lane lengths operated from other ends. We have also used this system to provide storage to an area previously only used for marshalling in lane lengths up to 48 pallets deep.
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space utilisation of floor area | |||||
| Utilisation of storage cube | |||||
| Access to individual carton loads | |||||
| Speed of access & throughput | |||||
| Efficiency in stock control | |||||
| Specialised handling equipment | None Required | ||||
| Ease & speed of relocation | |||||
| Adjustability of beam locations | |||||
Book a FREE Healthcheck
Read Our Blog

6 Ways To Increase Storage Space In The Warehouse
Available space inevitably gets used up under normal operating conditions. It’s almost a law of nature, just like Parkinson’s Law (work expands to fill the available time). Opportunistic bulk discount purchases, overstocking, old stock or just inefficiency eats up costly space. Suddenly you cannot add new lines that consumers are demanding. Your stock represents too much capital.

5 Ways To Tell If You Need A New Warehouse Storage Design
Your warehouse represents the hub and therefore most important link in your supply chain. Yet, up to 3,000 hours are lost per year to warehouse inefficiencies that a redesign could fix. Is your warehouse currently suffering from any of the symptoms below? If so, a change in your warehouse design may very well be beneficial to your business.

Can Warehouse Storage Layout Design Impact Running A Warehouse Efficiently?
Is everything in your warehouse accessible and in the right place? Is your warehouse team able to carry out their tasks efficiently? If the layout design of your warehouse isn’t helping to allow the productivity of your staff and reduce your overheads, your warehouse storage layout design may need to change.
